40 what is the greenhouse effect
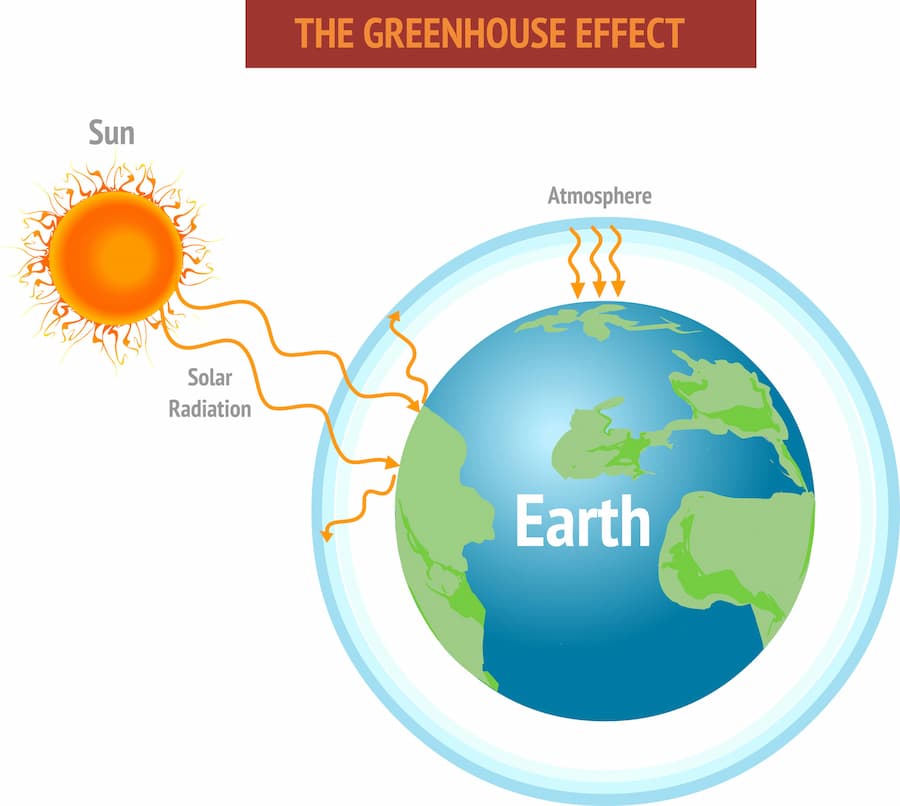
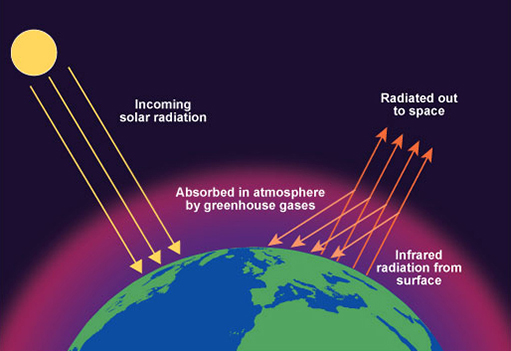
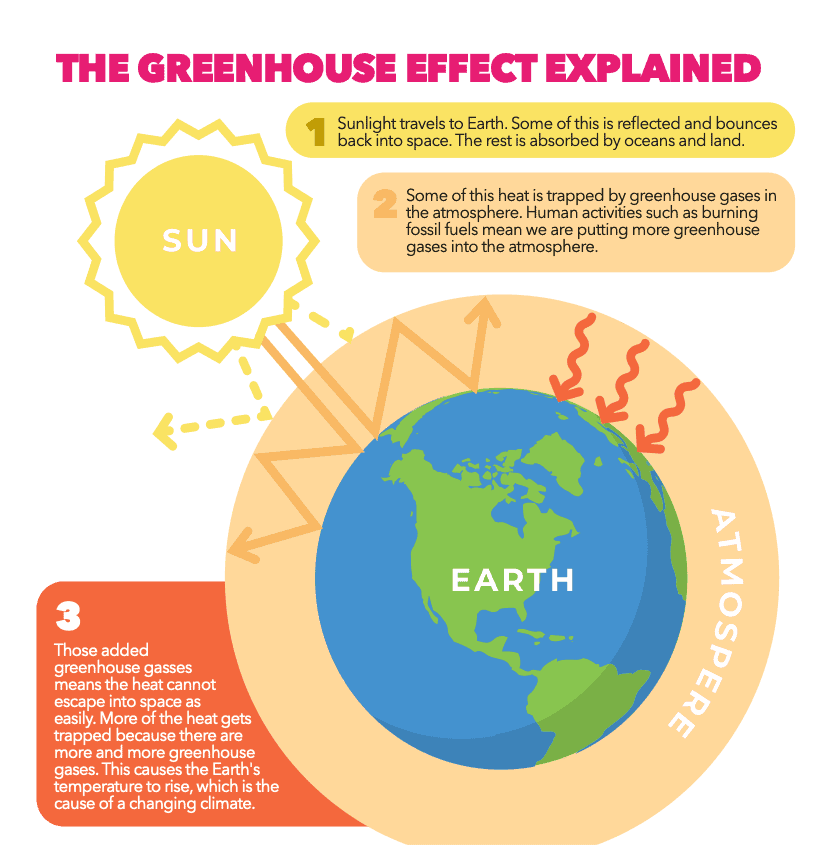
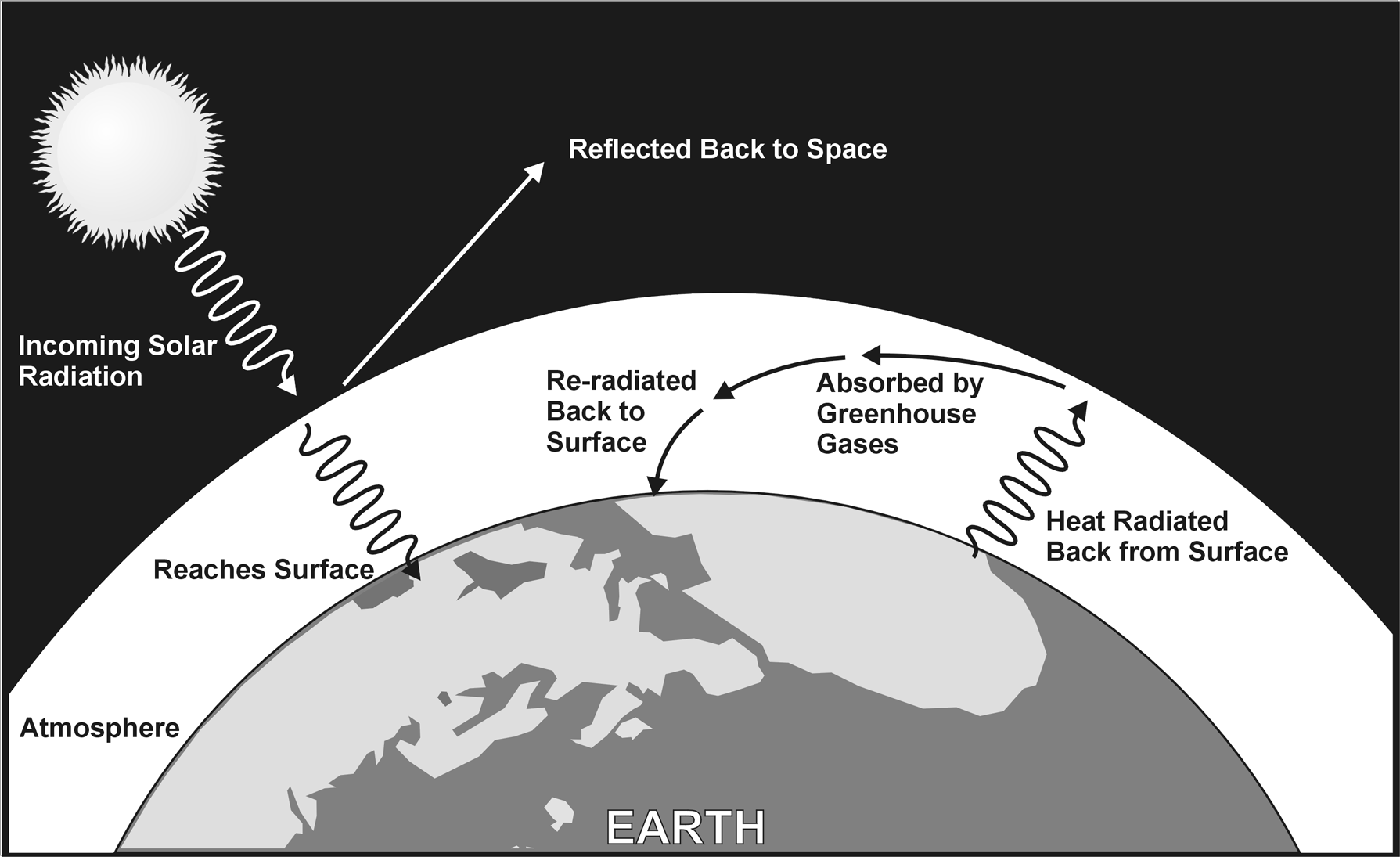
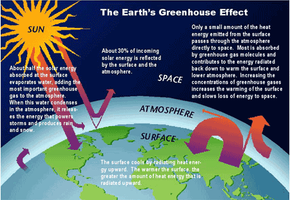
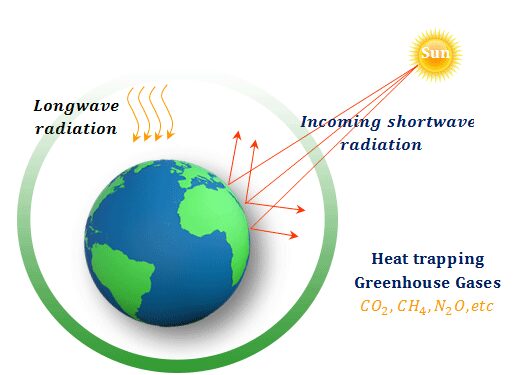
What Is the Greenhouse Effect? | NASA Climate Kids 09/03/2022 · The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth. Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases. During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere. Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight. Greenhouse effect - Understanding Global Change Greenhouse gases such as methane, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and water vapor significantly affect the amount of energy in the Earth system, even though they make up a tiny percentage of Earth’s atmosphere. Solar radiation that passes through the atmosphere and reaches Earth’s surface is either reflected or absorbed. Reflected sunlight doesn’t add any heat to the Earth system because this energy bounces back into space. However, absorbed sunlight increases the temperature of Earth’s surface, and the warmed surface re-radiatesas long-wave radiation (also known as infrared radiation). Infrared radiation is invisible to the eye, but we feel it as heat. If there were not any greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, all that heat would pass directly back into space. With greenhouse gases present, however, most of the long-wave radiation coming from Earth’s surface is absorbed and then re-radiated in all directions many times before passing back into space. Heat that is re-radiated downward...
Overview of Greenhouse Gases | US EPA Overview; Carbon Dioxide; Methane; Nitrous Oxide; Fluorinated Gases. Overview of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions in 2020. Total U.S. Emissions in ...

What is the greenhouse effect
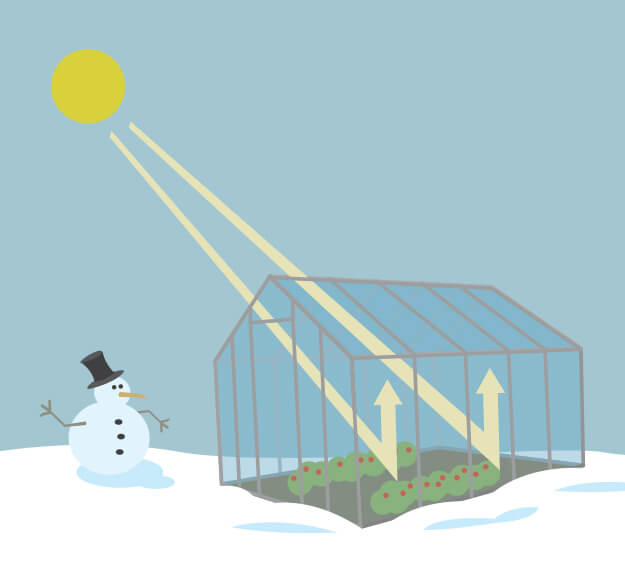
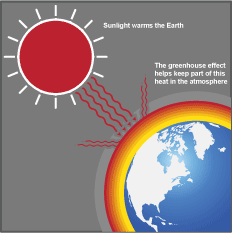
The Greenhouse Effect | NASA Space Place - NASA Science ... The Greenhouse Effect A greenhouse is for growing plants. It is made of glass or clear plastic to let in lots of sunlight. But why not just put the plants outside? A greenhouse stays warmer than the air outside. Instead of cooling off at night, it traps some of the heat inside to keep the plants warm. Greenhouse Gases - MIT Climate Portal 30/09/2020 · Greenhouse gases reflect infrared radiation, so some of the heat leaving the Earth bounces off the greenhouse gases in our atmosphere and comes back to the Earth’s surface. This is called the “greenhouse effect,” in a comparison to the heat-trapping glass on a greenhouse. The greenhouse effect is not a bad thing. What what is the greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when gases in Earth's atmosphere trap the Sun's heat. This process makes Earth much warmer than it would be without an atmosphere.
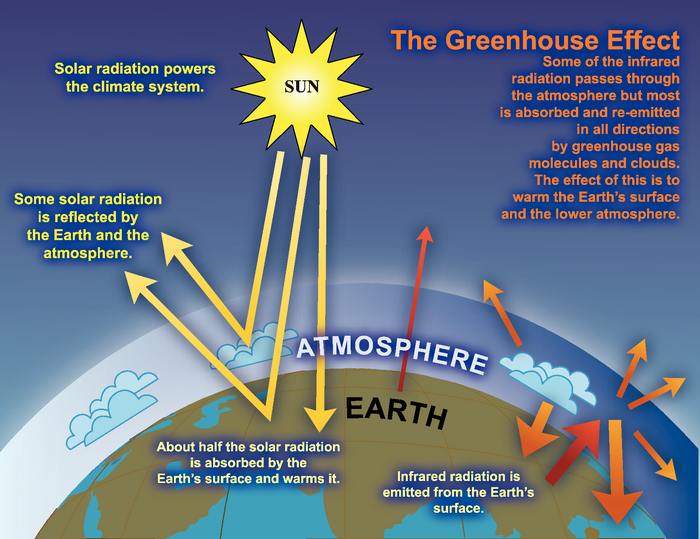
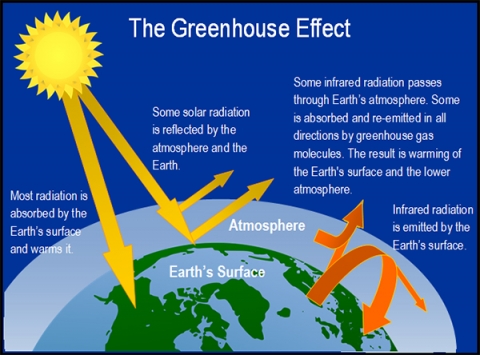
What is the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect - British Geological Survey The greenhouse effect: some of the infrared radiation from the Sun passes through the atmosphere, but most is absorbed and re-emitted in all directions by ... What is the Greenhouse Gas Effect? - CLEAR Center The term "greenhouse gas effect" generally has negative connotations these days, but that hasn't always been the case. The phenomena whereby certain gaseous compounds trap the sun's heat and act as a blanket of insulation around Earth is what makes our planet hospitable to life. What Is the Greenhouse Effect? - American Chemical Society Adding more greenhouse gases decreases the amount of infrared radiation energy leaving the atmosphere. To get the energy back in balance, the surface of the Earth has to warm up, so that it will emit more infrared energy, some of which will leave the atmosphere and compensate for the effect of the added greenhouse gases. What is the greenhouse effect? – Climate Change: Vital ... 18/04/2022 · The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by “greenhouse gases.” These heat-trapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them.
Consequences of the greenhouse effect - Iberdrola The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us. Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life. The greenhouse effect - Polluting the atmosphere - AQA ... How the greenhouse effect works Electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphere. The Earth absorbs most of the radiation and warms up. The Earth radiates energy... What Is the Greenhouse Effect? - YouTube Earth is a comfortable place for living things. It’s just the right temperatures for plants and animals – including humans – to thrive. Why is Earth so speci... Greenhouse Effect - ce. T Greenhouse Effect Heat transfer also plays an important role in controlling the temperature of the Earth. The Earth is heated by radiation from the Sun. Sunlight passes through the atmosphere and hits the ground, trees, houses and other things on the surface.
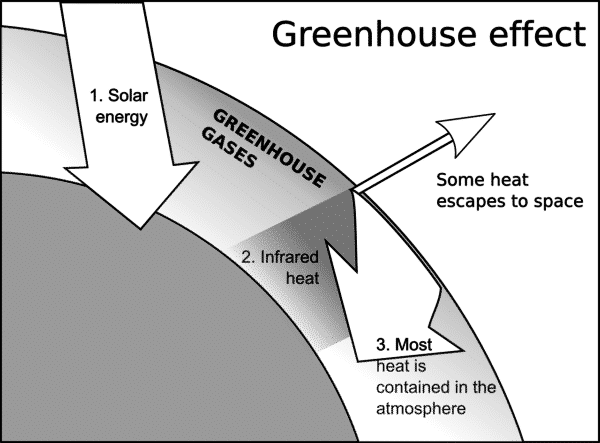
The Greenhouse Effect | Center for Science Education The greenhouse effect causes some of this energy to be waylaid in the atmosphere, absorbed and released by greenhouse gases. Without the greenhouse effect, Earth’s temperature would be below freezing. It is, in part, a natural process. However, Earth’s greenhouse effect is getting stronger as we add greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. what causes the greenhouse effect quizlet - Lisbdnet.com 7 What is the greenhouse effect for kids? 8 What are the causes and effects of the greenhouse effect? 9 What causes the greenhouse effect class 8? 10 What are the causes of global warming and greenhouse effect? 11 What are greenhouse gases quizlet? 12 Which of the following is a primary cause of the greenhouse effect? 13 Which of the following ... What is the Greenhouse Effect? — The More Complicated ... The runaway greenhouse effect is going to have massive repercussions on all of our lives, so it is important we understand it. I hope this information is helpful to you, feel free to leave any ... Climate Kids: What is the Greenhouse Effect? | Science ... The greenhouse effect is explained in this series of related questions and answers. This lesson is part of the Climate Kids website, a NASA education resource featuring articles, videos, images and games focused on the science of climate change.
what contributes to the enhanced greenhouse effect ... What Contributes To The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect??Global warming is attributed to the enhanced greenhouse effect. This is caused by the increased concentration and effect of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane and fluorocarbons. When fossil fuels are burned in power stations, vehicl
Greenhouse effect - Canada.ca These greenhouse gases absorb heat and radiate some of it back to the earth's surface, causing surface temperatures to be higher than they would otherwise be. The most important naturally occurring greenhouse gas is water vapour and it is the largest contributor to the natural greenhouse effect.
greenhouse effect | Definition, Diagram, Causes, & Facts ... greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect. The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear. French mathematician Joseph …
Advantages or Disadvantages of the Greenhouse Effect | by ... Greenhouse effect is the mechanism by which thermal radiation from earth's surface is reabsorbed by greenhouse gases and redirected in all directions. Some of the major green house gases are water...
The Greenhouse Effect and our Planet | National Geographic ... The Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change Even slight increases in average global temperatures can have huge effects. Perhaps the biggest, most obvious effect is that glaciers and ice caps melt faster than usual. The meltwater drains into the oceans, causing sea levels to rise. Glaciers and ice caps cover about 10 percent of the world's landmasses.
What is the greenhouse effect? - Sustainability for all What is the greenhouse effect? The greenhouse effect is a natural and necessary process that is negatively powered by man with disastrous consequences Do you know what the greenhouse effect is? It is the natural phenomenon that allows our planet to maintain the necessary conditions to harbor life.
Understanding climate change - DAWE - Environment.gov.au Oct 19, 2021 — Greenhouse gas effect ... The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface. When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's ...
The Greenhouse Effect | Center for Science Education The Greenhouse Effect Energy from the Sun that makes its way to Earth can have trouble finding its way back out to space. The greenhouse effect causes some of this energy to be waylaid in the atmosphere, absorbed and released by greenhouse gases. Without the greenhouse effect, Earth's temperature would be below freezing.
greenhouse effect | Definition, Diagram, Causes, & Facts greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect. The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear.
What Is the Greenhouse Effect? | NASA Climate Kids As you might expect from the name, the greenhouse effect works … like a greenhouse! A greenhouse is a building with glass walls and a glass roof. Greenhouses are used to grow plants, such as tomatoes and tropical flowers. A greenhouse stays warm inside, even during the winter. In the daytime, sunlight shines into the greenhouse and warms the plants and air inside. At nighttime, it's colder outside, but the greenhouse stays pretty warm inside. That's because the glass walls of the greenhouse trap the Sun's heat. The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth. Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases. During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere. Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight. At night, Earth's surface cools, releasing heat back into the air. But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. That's what keeps our Earth...
Greenhouse effect - Wikipedia The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when energy from a planet's sun goes through its atmosphere and warms the planet's surface, but the atmosphere prevents the heat from returning directly to space, resulting in a warmer planet. Light arriving from our Sun passes through Earth's atmosphere and warms its surface.
What is the greenhouse effect? - Inside Climate News This trapping of thermal radiation or heat in the Earth's atmosphere is called the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect makes Earth habitable for humans. If Earth's atmosphere didn't trap heat,...
What is the greenhouse effect? - NASA Climate Change Mar 23, 2022 · The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by “greenhouse gases.” These heat-trapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxides, and water vapor.
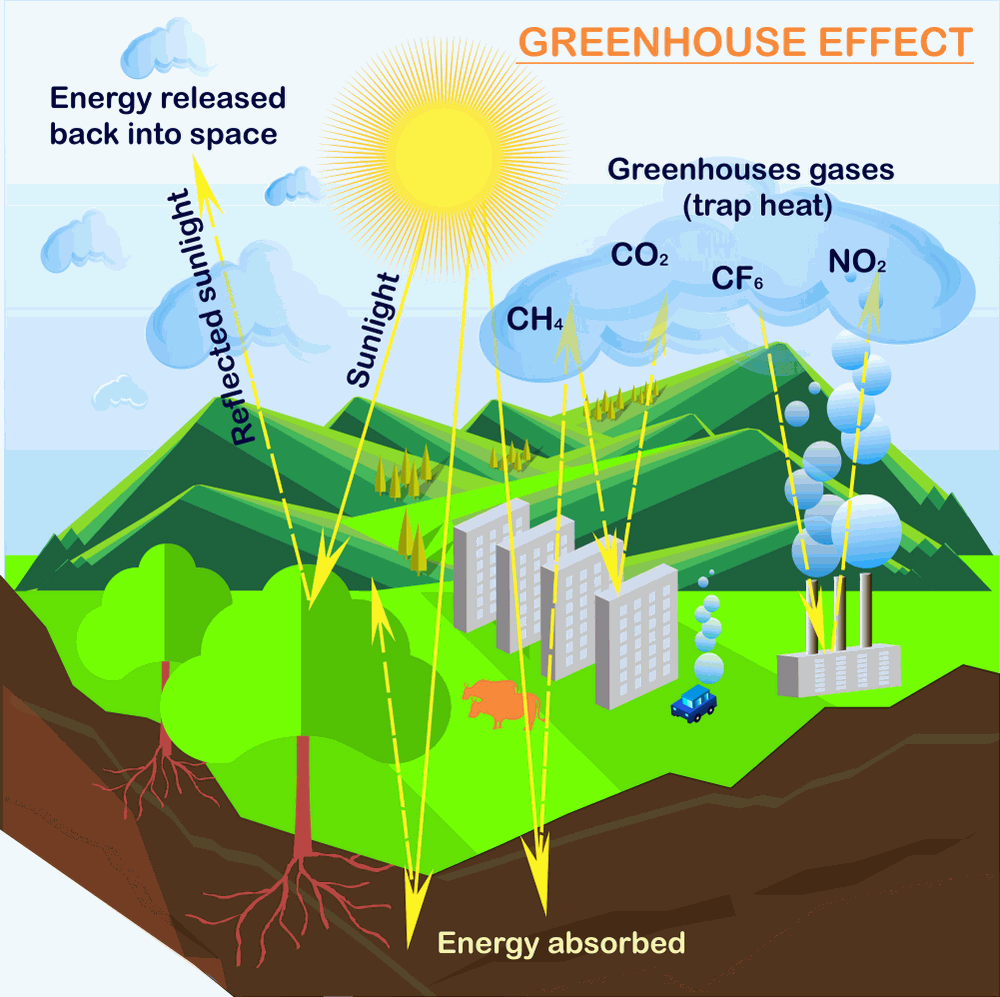
CILab: Greenhouse Gases Effect on Global Warming The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space. Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space. The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane ...
Greenhouse effect Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster : warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as earth or venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back …
Greenhouse Effect 101 | NRDC Jul 16, 2019 — The main gases responsible for the greenhouse effect include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor (which all occur naturally) ...
Greenhouse Effect - phet.colorado.edu Greenhouse Effect - phet.colorado.edu
Greenhouse effect Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster 10/12/2021 · The meaning of GREENHOUSE EFFECT is warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is …
Greenhouse Effect - National Geographic Society The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth’s atmosphere. These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinated gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). Greenhouse gases let the sun’s light shine onto the Earth’s surface, but they trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphere.
Greenhouse Effect - Meaning, Causes, Consequences and ... Greenhouse Effect is the process of heating of the surface of Earth till the troposphere. It happens because of higher concentration of carbon dioxide, water vapour, methane and other gases. Sunlight heats up Earth's surface, and subsequently, the energy is reflected back to space in the form of infrared radiation.
Greenhouse Effect - GeeksforGeeks The greenhouse effect is the consequence of the variation of λ max with temperature (i.e. Wien's law). In a greenhouse, the incident radiation from the sun is most intense at m = 4.83 × 10 m and passes through glass more easily.
What Is the Greenhouse Effect? - Climate Reality The process is called the greenhouse effect because the exchange of incoming and outgoing radiation that warms the planet works in a similar way to a greenhouse. Picture this: a greenhouse is so successful at growing plants year-round, even when it's too cold outside for some plants to typically thrive. How?
What is the Greenhouse Effect? | Global Warming | Live Science The greenhouse effect The exchange of incoming and outgoing radiation that warms the Earth is often referred to as the greenhouse effect because a greenhouse works in much the same way. Incoming UV...
What Is Greenhouse Effect? - Definition, Causes And Effects "Greenhouse effect is the process by which radiations from the sun are absorbed by the greenhouse gases and not reflected back into space. This insulates the surface of the earth and prevents it from freezing." What is the Greenhouse Effect? A greenhouse is a house made of glass that can be used to grow plants.
The Greenhouse Effect | NASA Space Place – NASA Science ... 07/04/2022 · The Greenhouse Effect. Life in a greenhouse? How ghastly! A greenhouse is for growing plants. It is made of glass or clear plastic to let in lots of sunlight. But why not just put the plants outside? A greenhouse stays warmer than the air outside. Instead of cooling off at night, it traps some of the heat inside to keep the plants warm.
What what is the greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when gases in Earth's atmosphere trap the Sun's heat. This process makes Earth much warmer than it would be without an atmosphere.
Greenhouse Gases - MIT Climate Portal 30/09/2020 · Greenhouse gases reflect infrared radiation, so some of the heat leaving the Earth bounces off the greenhouse gases in our atmosphere and comes back to the Earth’s surface. This is called the “greenhouse effect,” in a comparison to the heat-trapping glass on a greenhouse. The greenhouse effect is not a bad thing.
The Greenhouse Effect | NASA Space Place - NASA Science ... The Greenhouse Effect A greenhouse is for growing plants. It is made of glass or clear plastic to let in lots of sunlight. But why not just put the plants outside? A greenhouse stays warmer than the air outside. Instead of cooling off at night, it traps some of the heat inside to keep the plants warm.
























0 Response to "40 what is the greenhouse effect"
Post a Comment